CHRONIC URTICARIA – Characteristics
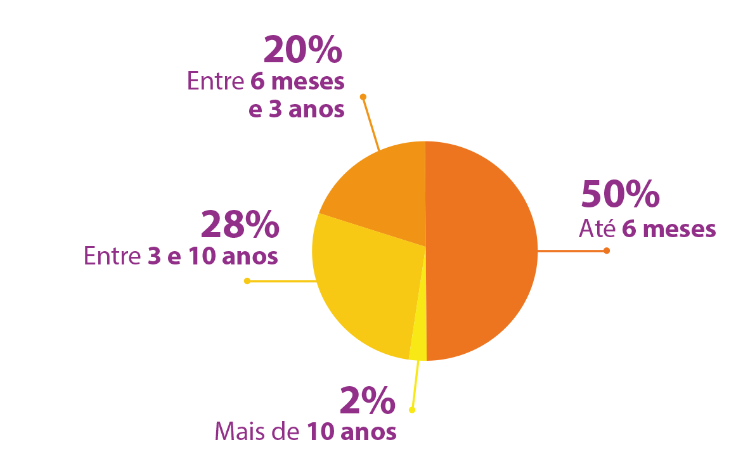
Urticaria is classified as chronic if its flares last for more than six weeks, in most of the week days. This is a self-limited disease, which resolves within three years in 70% of the cases.
The duration of the disease may vary, as shown on the illustration below:
Chronic urticaria can be subdivided into two broad groups: spontaneous urticaria and induced urticaria.
CHRONIC URTICARIA CLASSIFICATION
SPONTANEOUS
INDUCED
PHYSICAL
- Dermographism
- Cold urticaria
- Delayed-pressure urticaria
- Solar uticaria
- Localized-heat urticaria
- Vibratory angioedema
OTHER
- Cholinergic
- Aquagenic
- Contact wheals

Chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU)
CHRONIC SPONTANEOUS URTICARIA (CSU)
This is the urticaria subtype whose onset does not have any flare-triggering factor. Patients keep seeking for a cause, but can never find one. About 60% of all chronic urticaria cases are spontaneous. It predominantly affects middle-age women, or 1-2% of the world population. There is no scientific explanation for its occurrence, because its causative mechanisms are not clearly known by medicine. Current scientific studies still report the potential of part of the spontaneous urticaria being an autoimmune disease; in this case, autoantibodies – or antibodies produced by our own bodies – are produced, therefore causing urticaria. To support this assumption, there is an observed association of that kind of urticaria with other autoimmune diseases, i.e., a CSU patient usually has other autoimmune diseases, with the most common one being the Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
It is important to highlight that there is currently no single commercially-available test to confirm the presence of autoantibodies as a causative factor for spontaneous chronic urticaria. It must be emphasized that the treatment of other potentially concurrent autoimmune diseases does not improve urticaria symptoms – in these cases, urticaria requires a specific treatment.

CHRONIC INDUCED URTICARIA
This is the type of urticaria resulting from an external triggering factor known as rubbing, pressure, vibration, localized heat, cold, increased body temperature, or by contact to water or other substances. Consistently to the specific cause, it will be named differently – for example, if caused by rubbing, it will be called dermographism; if it is caused by increased body temperature, it will be
called cholinergic urticaria. Some of them –caused by physical stimuli – were called physical urticaria in the past.
In induced urticaria, flares are short in duration, lasting less than 1 hour – except for delayed-pressure and contact urticaria, which can last longer.
Many patients have more than one type of urticaria. They can have chronic spontaneous urticaria associated to induced urticaria. Or, also, have two or more different induced urticarias, such as dermographism + cholinergic urticaria.
There is also a variation of the cholinergic urticaria and aquagenic urticaria, which present only with itching, but no visible hives, which are respectively called cholinergic pruritus and aquagenic pruritus.
Types of Induced Urticarias
| Types | What does it cause? How long after? | Prevalence | Special characteristics of injuries | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cold urticaria | contact of the skin with cold (wind, fluids or surfaces), minutes after the stimulation | common | wheals in the exposure areas to cold can generalize and result in a much severe case | |
| Delayed pressure urticaria | pressure over the skin, 4-8 hours after stimulation | common | big wheals in the pressure areas with pain or burning. Lasts for hours. | |
| Localized heat urticaria | contact of the skin with hot objects, minutes after stimulation | very rare | wheals only in the exposure areas to heat | |
| Solar urticaria | incidence of light over the skin, minutes after stimulation | rare | wheals only in the exposure areas to light | |
| Dermographism | friction on the skin, minutes after stimulation | common | wheals line shaped or itching | |
| Vibratory angioedema | vibration, minutes after stimulation | very rare | big swelling in the vibratory area, with pain or burning | |
| Aquagenic urticaria | contact of the skin with water at any temperature, minutes after stimulation | Munutos após o estímulo | rare | small wheals or redness in the contact areas with water |
| Cholinergic urticaria | increased body temperature (hot baths, physical activity, stress), minutes after stimulation | Common | redness or minor wheals, mainly in the upper body | |
| Contact wheals | contact of the skin with certain substances (food, plants, chemical products, fruits), until 30 minutes after stimulation | common | Wheals in the contact areas with the substance, can generalize through the whole body, causing severe cases with angioedema |
For more detailed information on the different types of induced chronic urticaria, please click on:
References:
J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014 May;133(5):1270-7
Allergy. 2014 Jul; 69(7):868-87
Acta Derm Venereol 2017; 97: XX–XX; Epub ahead of print Jun 28, 2016
Allergy. 2009: 64: 1715–1721 _ 2009
Immunol Allergy Clin N Am 34 (2014) 53–72